OTel Java 探针如何做到依赖的隔离
背景与问题
目前,在Java语言中对应用做分布式调用链路追踪通常通常会使用基于javaagent技术来实现,javaagent可以无侵入地对目标代码进行插桩,相当于在用户或者框架的代码的特定方法前后插入了一段逻辑,以完成观测数据收集的相关需求。javaagent技术虽然是无侵入的,用户无需改动其业务代码,但是其也引入了很多的问题与风险,其中一个很重要的风险就是,javaagen插桩代码中引入的依赖如何才能不与用户引入的依赖相冲突,具体点就是:
- 如何保证agent里面用的依赖包和用户引的不冲突:比如agent中和用户的代码都引入了fastjson,如果agent中的版本把用户引入的fastjson给冲掉了,会不会导致用户业务代码报错?
- 如何保证agent中的sdk与与用户用的sdk不冲突:用户在进行分布式调用链路追踪时,通常会对业务中的一些重要业务逻辑通过sdk进行埋点收集,然而javaagent在埋点时也会通过该sdk进行埋点收集,如何保证两套sdk之间的兼容性?
带着上面两个问题,我们来看一下opentelemetry社区的javaagent实现是怎么做的。
OTel Java探针项目结构概述
在介绍OTel的javaagent如何实现依赖隔离之前,首先来介绍一下OTel探针整体的项目结构与每个模块引入依赖的情况:

OTel探针的主要模块有下面几个,其中:
- javaagent-bootstrap:包含javaagent的初始化逻辑(即premain等方法)
- instrumentation-api:封装了一些在javaagent注入代码时的一些常用公共逻辑,比如开启/关闭某个span的逻辑
- instrumentation-api-semconv:封装了一些AttributesExtractor,这些Extractor的作用是提取出必要的属性以符合opentelemetry的规范
- javaagent-tooling:一些公共的工具类,比如json处理,http客户端等等
对于上面的每一个模块,其都会引入一些不同的依赖,举个例子:instrumentation-api以及instrumentation-api-semconv模块会引入opentelemetry sdk的api接口,javaagent-tooling模块则会引入opentelemetry sdk的实际sdk实现以及jackson等json库实现。
OTel探针隔离方式
类加载器隔离
在Java语言中,用来实现类的隔离最常见的方式就是使用不同的类加载器将类隔离开,OTel探针的类加载器结构如下图所示:
- 整个agent中,只有OpenTelemetryAgent这个类会侵入到用户的系统类加载器中,这个类是整个agent逻辑的入口(会触发这个类中的premain方法)
- agent用到的工具,依赖等等全部都会放在一个单独的并行URL Classloader(Agent Classloader)中,比如agent引入的json处理库,opentelemetry sdk的实际实现等等

- 一些封装好的公共方法以及公共接口,比如instrumentation-api,instrumentation-api-semconv等会注入到agent的bootstrap classloader中,这些方法会被插入到用户的代码中,所以要保证这些方法在哪里都是可见的。

那么具体实现的时候,怎么保证一些类被AgentClassloader加载,另一些类又被Bootstrap Classloader加载呢?毕竟这些类都是打在同一个jar包里面的。Opentelemetry的agent用了一个比较trick的办法:
OTel探针把打包后的javaagent包整个加入到bootstrap classloader的搜索路径中

这样,这个javaagent中里面所有的类都可以在bootstrap classloader中被找到,然而OTel agent还做了一个骚操作将一些类挪到AgentClassloader中:
在打包的时候,对于一些可能和用户依赖产生冲突的工具类(比如json处理类),OTel agent会把这些类编译后的class文件单独挪到一个inst目录下
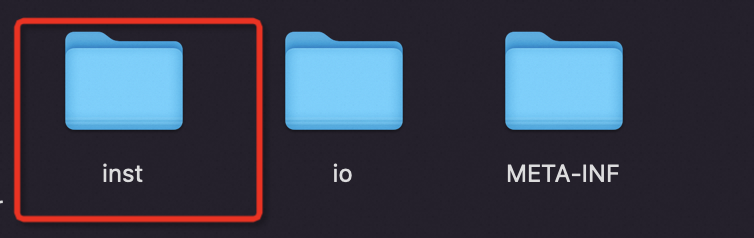
这个目录下,所有的.class文件都被重命名为.classdata,这样,在这个javaagent的jar包被加入到bootstrap classloader的搜索路径里面后,bootstrap classloader就没法识别这些.classdata文件,也就不会加载inst这个文件夹里面的类。

inst文件夹中的这些类将由一个单独的并行类加载器AgentClassloader来接管,这个classloader会把类的后缀改成.classdata之后在jar包的inst目录里面搜索,如果搜索到了对应的.classdata文件,则将其加载到AgentClassloader中。
/* * Copyright The OpenTelemetry Authors * SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0 */
package io.opentelemetry.javaagent.bootstrap;
import java.io.File;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.InputStream;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.net.MalformedURLException;import java.net.URL;import java.net.URLClassLoader;import java.net.URLConnection;import java.net.URLStreamHandler;import java.security.AllPermission;import java.security.CodeSource;import java.security.Permission;import java.security.PermissionCollection;import java.security.Permissions;import java.security.cert.Certificate;import java.util.Enumeration;import java.util.jar.JarEntry;import java.util.jar.JarFile;import java.util.jar.Manifest;import javax.annotation.Nullable;
/** * Classloader used to run the core agent. * * <p>It is built around the concept of a jar inside another jar. This class loader loads the files * of the internal jar to load classes and resources. */public class AgentClassLoader extends URLClassLoader {
// NOTE it's important not to use logging in this class, because this class is used before logging // is initialized
static { ClassLoader.registerAsParallelCapable(); }
private static final String AGENT_INITIALIZER_JAR = System.getProperty("OTel.javaagent.experimental.initializer.jar", "");
private static final String META_INF = "META-INF/"; private static final String META_INF_VERSIONS = META_INF + "versions/";
// multi release jars were added in java 9 private static final int MIN_MULTI_RELEASE_JAR_JAVA_VERSION = 9; // current java version private static final int JAVA_VERSION = getJavaVersion(); private static final boolean MULTI_RELEASE_JAR_ENABLE = JAVA_VERSION >= MIN_MULTI_RELEASE_JAR_JAVA_VERSION;
// Calling java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation#appendToBootstrapClassLoaderSearch // adds a jar to the bootstrap class lookup, but not to the resource lookup. // As a workaround, we keep a reference to the bootstrap jar // to use only for resource lookups. private final BootstrapClassLoaderProxy bootstrapProxy;
private final JarFile jarFile; private final URL jarBase; private final String jarEntryPrefix; private final CodeSource codeSource; private final boolean isSecurityManagerSupportEnabled; private final Manifest manifest;
// Used by tests public AgentClassLoader(File javaagentFile) { this(javaagentFile, "", false); }
/** * Construct a new AgentClassLoader. * * @param javaagentFile Used for resource lookups. * @param internalJarFileName File name of the internal jar * @param isSecurityManagerSupportEnabled Whether this class loader should define classes with all * permissions */ public AgentClassLoader( File javaagentFile, String internalJarFileName, boolean isSecurityManagerSupportEnabled) { super(new URL[] {}, getParentClassLoader()); if (javaagentFile == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Agent jar location should be set"); } if (internalJarFileName == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Internal jar file name should be set"); }
this.isSecurityManagerSupportEnabled = isSecurityManagerSupportEnabled; bootstrapProxy = new BootstrapClassLoaderProxy(this);
jarEntryPrefix = internalJarFileName + (internalJarFileName.isEmpty() || internalJarFileName.endsWith("/") ? "" : "/"); try { jarFile = new JarFile(javaagentFile, false); // base url for constructing jar entry urls // we use a custom protocol instead of typical jar:file: because we don't want to be affected // by user code disabling URLConnection caching for jar protocol e.g. tomcat does this jarBase = new URL("x-internal-jar", null, 0, "/", new AgentClassLoaderUrlStreamHandler(jarFile)); codeSource = new CodeSource(javaagentFile.toURI().toURL(), (Certificate[]) null); manifest = jarFile.getManifest(); } catch (IOException e) { throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to open agent jar", e); }
if (!AGENT_INITIALIZER_JAR.isEmpty()) { URL url; try { url = new File(AGENT_INITIALIZER_JAR).toURI().toURL(); } catch (MalformedURLException e) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Filename could not be parsed: " + AGENT_INITIALIZER_JAR + ". Initializer is not installed", e); }
addURL(url); } }
private static ClassLoader getParentClassLoader() { if (JAVA_VERSION > 8) { return new PlatformDelegatingClassLoader(); } return null; }
private static int getJavaVersion() { String javaSpecVersion = System.getProperty("java.specification.version"); if ("1.8".equals(javaSpecVersion)) { return 8; } return Integer.parseInt(javaSpecVersion); }
@Override public Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve) throws ClassNotFoundException { // ContextStorageOverride is meant for library instrumentation we don't want it to apply to our // bundled grpc if ("io.grpc.override.ContextStorageOverride".equals(name)) { throw new ClassNotFoundException(name); }
synchronized (getClassLoadingLock(name)) { Class<?> clazz = findLoadedClass(name); // first search agent classes if (clazz == null) { clazz = findAgentClass(name); } // search from parent and urls added to this loader if (clazz == null) { clazz = super.loadClass(name, false); } if (resolve) { resolveClass(clazz); }
return clazz; } }
private Class<?> findAgentClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException { JarEntry jarEntry = findJarEntry(name.replace('.', '/') + ".class"); if (jarEntry != null) { byte[] bytes; try { bytes = getJarEntryBytes(jarEntry); } catch (IOException exception) { throw new ClassNotFoundException(name, exception); }
definePackageIfNeeded(name); return defineClass(name, bytes); }
return null; }
public Class<?> defineClass(String name, byte[] bytes) { return defineClass(name, bytes, 0, bytes.length, codeSource); }
@Override protected PermissionCollection getPermissions(CodeSource codeSource) { if (isSecurityManagerSupportEnabled) { Permissions permissions = new Permissions(); permissions.add(new AllPermission()); return permissions; }
return super.getPermissions(codeSource); }
private byte[] getJarEntryBytes(JarEntry jarEntry) throws IOException { int size = (int) jarEntry.getSize(); byte[] buffer = new byte[size]; try (InputStream is = jarFile.getInputStream(jarEntry)) { int offset = 0; int read;
while (offset < size && (read = is.read(buffer, offset, size - offset)) != -1) { offset += read; } }
return buffer; }
private void definePackageIfNeeded(String className) { String packageName = getPackageName(className); if (packageName == null) { return; } if (getPackage(packageName) == null) { try { definePackage(packageName, manifest, codeSource.getLocation()); } catch (IllegalArgumentException exception) { if (getPackage(packageName) == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to define package", exception); } } } }
private static String getPackageName(String className) { int index = className.lastIndexOf('.'); return index == -1 ? null : className.substring(0, index); }
private JarEntry findJarEntry(String name) { // shading renames .class to .classdata boolean isClass = name.endsWith(".class"); if (isClass) { name += getClassSuffix(); }
JarEntry jarEntry = jarFile.getJarEntry(jarEntryPrefix + name); if (MULTI_RELEASE_JAR_ENABLE) { jarEntry = findVersionedJarEntry(jarEntry, name); } return jarEntry; }
// suffix appended to class resource names // this is in a protected method so that unit tests could override it protected String getClassSuffix() { return "data"; }
private JarEntry findVersionedJarEntry(JarEntry jarEntry, String name) { // same logic as in JarFile.getVersionedEntry if (!name.startsWith(META_INF)) { // search for versioned entry by looping over possible versions form high to low int version = JAVA_VERSION; while (version >= MIN_MULTI_RELEASE_JAR_JAVA_VERSION) { JarEntry versionedJarEntry = jarFile.getJarEntry(jarEntryPrefix + META_INF_VERSIONS + version + "/" + name); if (versionedJarEntry != null) { return versionedJarEntry; } version--; } }
return jarEntry; }
@Override public URL getResource(String resourceName) { URL bootstrapResource = bootstrapProxy.getResource(resourceName); if (null == bootstrapResource) { return super.getResource(resourceName); } else { return bootstrapResource; } }
@Override public URL findResource(String name) { URL url = findJarResource(name); if (url != null) { return url; }
// find resource from agent initializer jar return super.findResource(name); }
private URL findJarResource(String name) { JarEntry jarEntry = findJarEntry(name); return getJarEntryUrl(jarEntry); }
private URL getJarEntryUrl(JarEntry jarEntry) { if (jarEntry != null) { try { return new URL(jarBase, jarEntry.getName()); } catch (MalformedURLException e) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Failed to construct url for jar entry " + jarEntry.getName(), e); } }
return null; }
@Override public Enumeration<URL> findResources(String name) throws IOException { // find resources from agent initializer jar Enumeration<URL> delegate = super.findResources(name); // agent jar can have only one resource for given name URL url = findJarResource(name); if (url != null) { return new Enumeration<URL>() { boolean first = true;
@Override public boolean hasMoreElements() { return first || delegate.hasMoreElements(); }
@Override public URL nextElement() { if (first) { first = false; return url; } return delegate.nextElement(); } }; }
return delegate; }
public BootstrapClassLoaderProxy getBootstrapProxy() { return bootstrapProxy; }
/** * A stand-in for the bootstrap class loader. Used to look up bootstrap resources and resources * appended by instrumentation. * * <p>This class is thread safe. */ public static final class BootstrapClassLoaderProxy extends ClassLoader { private final AgentClassLoader agentClassLoader;
static { ClassLoader.registerAsParallelCapable(); }
public BootstrapClassLoaderProxy(AgentClassLoader agentClassLoader) { super(null); this.agentClassLoader = agentClassLoader; }
@Override public URL getResource(String resourceName) { // find resource from boot loader URL url = super.getResource(resourceName); if (url != null) { return url; } // find from agent jar if (agentClassLoader != null) { JarEntry jarEntry = agentClassLoader.jarFile.getJarEntry(resourceName); return agentClassLoader.getJarEntryUrl(jarEntry); } return null; }
@Override protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException { throw new ClassNotFoundException(name); } }
private static class AgentClassLoaderUrlStreamHandler extends URLStreamHandler { private final JarFile jarFile;
AgentClassLoaderUrlStreamHandler(JarFile jarFile) { this.jarFile = jarFile; }
@Override protected URLConnection openConnection(URL url) { return new AgentClassLoaderUrlConnection(url, jarFile); } }
private static class AgentClassLoaderUrlConnection extends URLConnection { private final JarFile jarFile; @Nullable private final String entryName; @Nullable private JarEntry jarEntry;
AgentClassLoaderUrlConnection(URL url, JarFile jarFile) { super(url); this.jarFile = jarFile; String path = url.getFile(); if (path.startsWith("/")) { path = path.substring(1); } if (path.isEmpty()) { path = null; } this.entryName = path; }
@Override public void connect() throws IOException { if (!connected) { if (entryName != null) { jarEntry = jarFile.getJarEntry(entryName); if (jarEntry == null) { throw new FileNotFoundException( "JAR entry " + entryName + " not found in " + jarFile.getName()); } } connected = true; } }
@Override public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException { connect();
if (entryName == null) { throw new IOException("no entry name specified"); } else { if (jarEntry == null) { throw new FileNotFoundException( "JAR entry " + entryName + " not found in " + jarFile.getName()); } return jarFile.getInputStream(jarEntry); } }
@Override public Permission getPermission() { return null; }
@Override public long getContentLengthLong() { try { connect();
if (jarEntry != null) { return jarEntry.getSize(); } } catch (IOException ignored) { // Ignore } return -1; } }
// We don't always delegate to platform loader because platform class loader also contains user // classes when running a modular application. We don't want these classes interfering with the // agent. private static class PlatformDelegatingClassLoader extends ClassLoader {
static { // this class loader doesn't load any classes, so this is technically unnecessary, // but included for safety, just in case we every change Class.forName() below back to // super.loadClass() registerAsParallelCapable(); }
private final ClassLoader platformClassLoader = getPlatformLoader();
public PlatformDelegatingClassLoader() { super(null); }
@Override protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve) throws ClassNotFoundException { // prometheus exporter uses jdk http server, load it from the platform class loader // some custom extensions use java.sql classes, make these available to agent and extensions if (name != null && (name.startsWith("com.sun.net.httpserver.") || name.startsWith("java.sql."))) { return platformClassLoader.loadClass(name); } return Class.forName(name, false, null); }
private static ClassLoader getPlatformLoader() { /* Must invoke ClassLoader.getPlatformClassLoader by reflection to remain compatible with java 8. */ try { Method method = ClassLoader.class.getDeclaredMethod("getPlatformClassLoader"); return (ClassLoader) method.invoke(null); } catch (InvocationTargetException | NoSuchMethodException | IllegalAccessException exception) { throw new IllegalStateException(exception); } } }}shadow隔离
上面讲了一下如何通过类加载器来实现依赖的隔离,通过多个类加载器的分层,agent中引入的一些依赖就能很好的和用户引入的依赖隔离开,从而避免了对用户业务的影响。但是我们也注意到,我们还是把一些依赖加入到了bootstrap classloader,对于用户来说,bootstrap classloader他也是完全可见的,举个例子,用户他引入了opentelemetry sdk的api,这些api会在用户的类加载器中被加载,但是agent也在bootstrap classloader中引入了这些公共的api,根据双亲委派原则,在加载这些api时优先就会加载agent提供的opentelemetry api,这就会覆盖掉用户引入的opentelemetry api。
那么如何解决上面说的这个问题呢?答案是通过shadow机制。简单理解一下shadow机制,直白的说就是在所有的类文件中做了一次ctrl+R替换,把原来的包名替换为一个新的包名,

在OTel agent实现中,会把所有添加到bootstrap classloader中的类都进行一次shadow,这样用户引入的opentelemetry api就不会与agent引入的相冲突。
tasks.withType<ShadowJar>().configureEach { mergeServiceFiles() // Merge any AWS SDK service files that may be present (too bad they didn't just use normal // service loader...) mergeServiceFiles("software/amazon/awssdk/global/handlers")
exclude("**/module-info.class")
// rewrite dependencies calling Logger.getLogger relocate("java.util.logging.Logger", "io.opentelemetry.javaagent.bootstrap.PatchLogger")
if (project.findProperty("disableShadowRelocate") != "true") { // prevents conflict with library instrumentation, since these classes live in the bootstrap class loader relocate("io.opentelemetry.instrumentation", "io.opentelemetry.javaagent.shaded.instrumentation") { // Exclude resource providers since they live in the agent class loader exclude("io.opentelemetry.instrumentation.resources.*") exclude("io.opentelemetry.instrumentation.spring.resources.*") } }
// relocate(OpenTelemetry API) since these classes live in the bootstrap class loader relocate("io.opentelemetry.api", "io.opentelemetry.javaagent.shaded.io.opentelemetry.api") relocate("io.opentelemetry.semconv", "io.opentelemetry.javaagent.shaded.io.opentelemetry.semconv") relocate("io.opentelemetry.context", "io.opentelemetry.javaagent.shaded.io.opentelemetry.context") relocate("io.opentelemetry.extension.incubator", "io.opentelemetry.javaagent.shaded.io.opentelemetry.extension.incubator")
// relocate(the OpenTelemetry extensions that are used by instrumentation modules) // these extensions live in the AgentClassLoader, and are injected into the user's class loader // by the instrumentation modules that use them relocate("io.opentelemetry.extension.aws", "io.opentelemetry.javaagent.shaded.io.opentelemetry.extension.aws") relocate("io.opentelemetry.extension.kotlin", "io.opentelemetry.javaagent.shaded.io.opentelemetry.extension.kotlin")
// this is for instrumentation of opentelemetry-api and opentelemetry-instrumentation-api relocate("application.io.opentelemetry", "io.opentelemetry") relocate("application.io.opentelemetry.instrumentation.api", "io.opentelemetry.instrumentation.api")
// this is for instrumentation on java.util.logging (since java.util.logging itself is shaded above) relocate("application.java.util.logging", "java.util.logging")}shadow后的自埋点实现
在进行shadow后,解决了bootstrap classloader中依赖覆盖的问题,但是还有一个corner case没有解决:在OTel中,通常会对OTel的sdk进行自埋点,以解决同时使用opentelemetry sdk以及opentelemetry javaagent时可能遇到的问题。举个例子,如果用户使用opentelemetry sdk更新了span的route状态,由于用户使用的HttpRouteState类是在系统类加载器中的,而OTel agent使用的HttpRouteState是在bootstrap类加载器中的,所以用户在sdk中更新路由是对javaagent无效的,为了保持用户sdk中的路由状态与javaagent是一致的,opentelemetry agent这时就需要对用户引入的opentelemetry sdk做埋点增强,在其更新sdk中的路由状态后顺带更新agent中的路由状态。
/* * Copyright The OpenTelemetry Authors * SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0 */
package io.opentelemetry.javaagent.instrumentation.instrumentationapi;
import static net.bytebuddy.matcher.ElementMatchers.named;import static net.bytebuddy.matcher.ElementMatchers.takesArgument;
import application.io.opentelemetry.api.trace.Span;import application.io.opentelemetry.context.Context;import io.opentelemetry.javaagent.extension.instrumentation.TypeInstrumentation;import io.opentelemetry.javaagent.extension.instrumentation.TypeTransformer;import io.opentelemetry.javaagent.instrumentation.opentelemetryapi.context.AgentContextStorage;import io.opentelemetry.javaagent.instrumentation.opentelemetryapi.trace.Bridging;import net.bytebuddy.asm.Advice;import net.bytebuddy.description.type.TypeDescription;import net.bytebuddy.matcher.ElementMatcher;
final class HttpRouteStateInstrumentation implements TypeInstrumentation {
@Override public ElementMatcher<TypeDescription> typeMatcher() { return named("application.io.opentelemetry.instrumentation.api.internal.HttpRouteState"); }
@Override public void transform(TypeTransformer transformer) { transformer.applyAdviceToMethod( named("update") .and(takesArgument(0, named("application.io.opentelemetry.context.Context"))) .and(takesArgument(1, int.class)) .and(takesArgument(2, String.class)), this.getClass().getName() + "$UpdateAdvice"); transformer.applyAdviceToMethod( named("updateSpan") .and(takesArgument(0, named("application.io.opentelemetry.context.Context"))) .and(takesArgument(1, named("application.io.opentelemetry.api.trace.Span"))), this.getClass().getName() + "$UpdateSpanAdvice"); }
@SuppressWarnings("unused") public static class UpdateAdvice { @Advice.OnMethodEnter(suppress = Throwable.class) public static void onEnter( @Advice.Argument(0) Context applicationContext, @Advice.Argument(1) int updatedBySourceOrder, @Advice.Argument(2) String route) {
io.opentelemetry.context.Context agentContext = AgentContextStorage.getAgentContext(applicationContext);
io.opentelemetry.instrumentation.api.internal.HttpRouteState agentRouteState = io.opentelemetry.instrumentation.api.internal.HttpRouteState.fromContextOrNull( agentContext); if (agentRouteState == null) { return; }
agentRouteState.update(agentContext, updatedBySourceOrder, route); } }
@SuppressWarnings("unused") public static class UpdateSpanAdvice { @Advice.OnMethodEnter(suppress = Throwable.class) public static void onEnter( @Advice.Argument(0) Context applicationContext, @Advice.Argument(1) Span applicationSpan) {
io.opentelemetry.context.Context agentContext = AgentContextStorage.getAgentContext(applicationContext); io.opentelemetry.instrumentation.api.internal.HttpRouteState.updateSpan( agentContext, Bridging.toAgentOrNull(applicationSpan)); } }}opentelemetry agent对sdk进行埋点的部分代码如上所示,看到这个代码我们可能会很疑惑,为什么我们要对application.io.opentelemetry.instrumentation.api.internal.HttpRouteState这个类进行埋点增强呢?因为io.opentelemetry.api开头的类都在bootstrap classloader里面,根据本文之前的讲解这些类会被shadow为以io.opentelemetry.javaagent.shaded.io.opentelemetry.api打头的类。所以如果我们在代码里面直接使用io.opentelemetry.instrumentation.api开头的类,实际上这些类都会被shadow为以io.opentelemetry.javaagent.shaded.io.opentelemetry.api开头的类,这样埋点的实际上都是在埋agent中shadow后的opentelemetry sdk,而非用户引入的sdk。
OTel agent在编译早期把以io.opentelemetry.api开头的类先进行了一次shadow,shadow为以application.io.opentelemetry.instrumentation.api开头的类。
 此后对
此后对application.io.opentelemetry.instrumentation.api.internal.HttpRouteState进行埋点,最后打包的时候再unshadow一次。

最后实际打进agent包的代码就是对io.opentelemetry.instrumentation.api.internal.HttpRouteState进行埋点了。
通过以上,我们就实现了对用户引入的opentelemetry sdk进行自埋点。
总结
OTel javaagent主要通过类加载隔离以及shadow隔离的方式来隔离用户与OTel javaagent的依赖,从而解决二者的依赖冲突问题。首先通过类加载器,把OTel javaagent引入的大部分私有依赖都隔离到一个新的类加载器中,而对于一些公共的依赖,OTel javaagent仍会把他加载到bootstrap classloader中,这时候就需要使用shadow机制来对bootstrap中的依赖进行进一步的隔离。